Three new developments have been unveiled by the DeepMind robotics team, which claims they will enable faster, safer, and better decision-making by robots in the wild. One uses a “Robot Constitution” to collect training data so that your robot office helper can provide you extra printer paper without running over a human coworker who happens to be in the way.
In order to comprehend its surroundings, adjust to new situations, and choose relevant tasks, Google’s AutoRT data collection system can collaborate with a large language model (LLM) and visual language model (VLM). The “Safety-focused prompts” in the Robot Constitution, which is modeled after Isaac Asimov’s “Three Laws of Robotics,” tell the LLM not to select activities involving people, animals, sharp items, or even electrical appliances.
To enhance safety measures, DeepMind integrated a physical kill switch that human operators can use to deactivate the robots, and configured the robots to halt automatically if the force applied to their joints exceeds a predetermined threshold. Google conducted approximately 77,000 trials with a fleet of 53 AutoRT robots over the course of seven months, spread across four distinct office buildings. While some robots were remotely handled by humans, others were driven by scripts or ran entirely on their own utilizing Google’s Robotic Transformer (RT-2) artificial intelligence learning model.
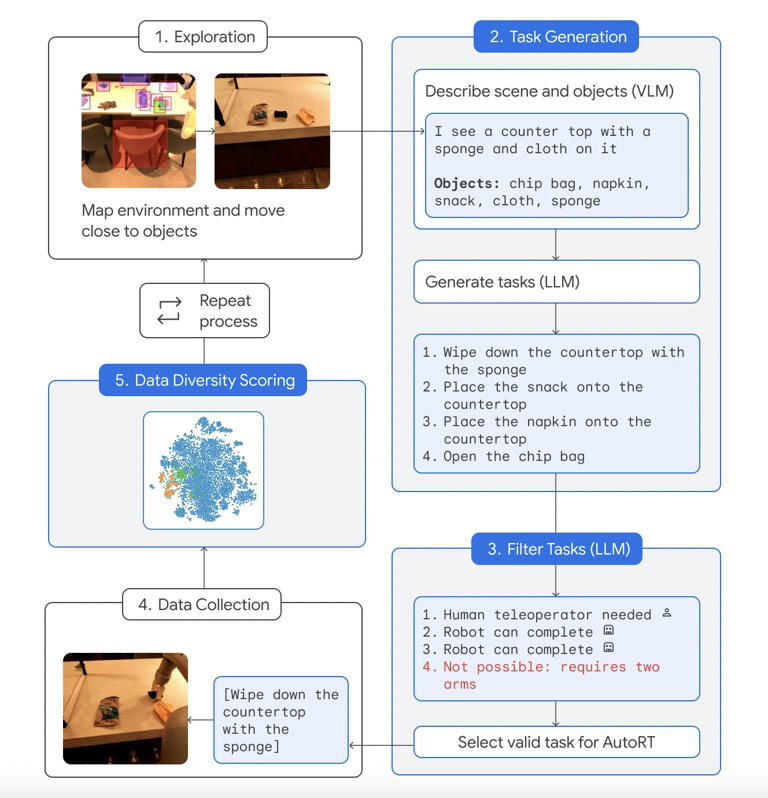
The trial’s robots, which are limited to a camera, robotic arm, and mobile base, appear more functional than ostentatious. “To comprehend its surroundings and the objects it can see, the system employs a VLM for every robot. As stated in Google’s blog post, “Next, an LLM acts as a decision-maker to choose an appropriate task for the robot to carry out and suggests a list of creative tasks that the robot could carry out, such as ‘Place the snack onto the countertop.”
SARA-RT, a neural network architecture created by DeepMind, is another piece of new technology that aims to improve the accuracy and speed of the Robotic Transformer RT-2. Additionally, it unveiled RT-Trajectory, which enhances 2D outlines to assist robots in carrying out particular physical duties, like cleaning down tables.
Though it seems like a long way off, robots that can serve drinks and fluff pillows on their own may have been trained using a technique similar to AutoRT.








