Google LLC has detailed Pathways, an in-house artificial intelligence project that aims to facilitate the development of neural networks that can learn thousands and possibly millions of tasks.
Jeff Dean, senior vice president of Google Research, featured a blog post on Thursday that outlined the company’s work on Pathways. The executive described the technology as “next generation artificial intelligence architecture” being developed by several different teams.
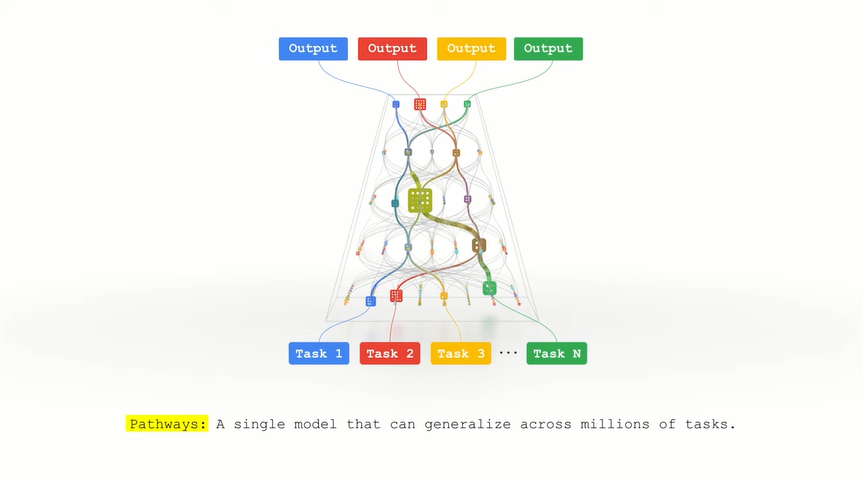
Today’s AI models can for the most part only be trained for a single task. For example, if a neural network that was originally trained to correct spelling mistakes is retrained to recognize grammatical errors, it is likely to “forget” its knowledge of correcting spelling mistakes. Google is developing Pathways to be more versatile. The technology, Dean wrote, will make it possible to create neural networks that can learn up to millions of different tasks.
Google’s plans to develop multipurpose AI software include equipping neural networks with multiple “skills,” the executive wrote. The search giant believes that combining these skills in different ways would allow it to tackle a wide variety of tasks. “That way, what a model learns by training a task, such as learning how aerial imagery can predict the elevation of a landscape, could help them learn another task, such as predicting how floods will flow through that terrain. “Dean explains.
Also in the interest of the versatility of artificial intelligence software, Google is developing Pathways to take advantage of different types of data. Today, a typical neural network can handle text, audio, or video, but not all three. Build neural networks that can draw on multiple types of information to make more accurate decisions. The result is a model that is more insightful and less prone to errors and bias, wrote Dean.
Google also hopes to make AI models more efficient.
A neural network consists of artificial neurons, bits of code, each of which performs a small part of the task for which the neural network is responsible. Often an AI does not have to use all of its artificial neurons for a calculation, but only a limited subset, but current AI models often fire all of their artificial neurons anyway when they perform calculations, even those that they do not use, which unnecessarily increases the number of neurons Infrastructure requirements.
Google hopes to implement an approach with Pathways that allows only those parts of a neural network to be activated that are absolutely necessary for a specific task. A big advantage of this type of architecture is that it can not only learn different tasks better, but is also faster and much more energy-efficient because we don’t activate the entire network for every task, Dean explained.
Google has already applied the concept in various artificial intelligence projects. Switch Transformer, a natural language processing model detailed by the company unveiled earlier this year, uses a technique called sparse activation to limit the number of artificial neurons used in computations. The transformation and another AI model called GShard that uses a similar technology use a tenth of the energy it would without the tech.
Google has been working on building more versatile neural networks for years. In 2016, the company’s researchers updated the AI that powers Google Translate with the ability to translate text between two languages, even if it wasn’t specially trained to do so. The AI research arm of Alphabet Inc., the parent company of Google, has developed an AI system that can learn a number of different games, including chess and Go.
Others in the machine learning ecosystem are also working on building multipurpose neural networks. Last year, OpenAI detailed an artificial intelligence system called GPT3 that is capable of performing tasks ranging from writing code to creating essays on business topics. They, in turn, have developed an approach that makes it possible to divide a neural network into several segments, each of which specializes in a different task.
There could be significant business benefits for Google in developing multipurpose AI that can perform thousands or millions of tasks.
Autonomous vehicles like that of Google’s sister company Waymo have to perform numerous computing tasks in order to convert their sensor data into driving decisions. Each computing task is often carried out by a separate neural network. Operate a large number of AI models on your on-board computer.Replacing multiple AI models with a single multipurpose neural network, like the one Google is trying to build through its Pathways initiative, could increase processing efficiency and help Waymo improve its autonomous driving stack.
In the public cloud, providing more versatile neural networks to customers could help Google make its managed artificial intelligence services more competitive. And, in the future, Pathways may also enable the company to improve its consumer services, especially Google search. Use of AI to process user inquiries.
Paths will allow a single AI system to generalize thousands or millions of tasks, understand different types of data, and do so with remarkable efficiency, wrote Dean. The goal, according to the executive, is “to lead us from the era of single-purpose models that simply recognize patterns to one in which more universal intelligent systems reflect a deeper understanding of our world and can adapt to new needs.”




