Key Learnings:
- Spot trading in cryptocurrencies entails purchasing or selling of an asset at the going rate for prompt delivery.
- To pay for trade in cryptocurrency margin trading, borrowed money is used. Therefore, the main distinction between margin trading and spot trading is the use of leverage.
- Spot trading is easier, but margin trading has the potential to magnify profits under certain conditions. Leverage, however, has a flip side in that it can also magnify losses.
- Which one to select mostly depends on the trader’s particular situation and risk tolerance.
What Is Spot Crypto Trading?

The spot market is where spot trading happens. Spot markets are available not only for cryptocurrencies but also for stocks, foreign exchange, commodities, and bonds, among other asset types.
The spot market is where traders purchase and sell assets (in the case of cryptocurrencies, tokens) at the going rate for delivery right away or very soon (i.e., within a few days). The term “spot” refers to the process of transacting and accepting ownership of an asset immediately. The spot price, trade date, and settlement date are the three crucial ideas in spot trading.
Spot value
The price at which a spot deal is carried out is the spot price, which is the asset’s current market value. By publishing their buy or sell orders, which include the price and quantity at which they desire to transact, buyers and sellers establish the spot price. As new orders are placed and existing ones are filled, the spot price changes.
Buying date
The trade order is carried out in the market on this day. In essence, it begins and records the transaction.
Date of settlement
The assets involved in the transaction are actually transferred on the settlement date, also known as the spot date. Depending on the type of market being traded, the interval between the trade date and settlement date may be on the same day (for some money-market assets, for example) or a few days (e.g., typically two days for stocks). For cryptocurrency, it usually happens on the same day, though it may differ amongst exchanges or trading platforms.
Spot trading is immediate, thus a trader needs to have the whole amount available to cover the trade. To acquire $1,000 worth of Bitcoin (BTC), for instance, a trader must have the full $1,000 in their account; otherwise, the exchange or trading platform won’t perform the trade.
What Is Margin Trading in Crypto?
Margin trading is the practice of funding a deal with borrowed money. Therefore, the primary distinction between margin trading and spot trading is that the former enables the trader to open a position without having to cover the entire cost out of their own pocket. Leverage, margin, collateral, and liquidation are the crucial terms to comprehend in margin trading.
Leverage
This refers to using borrowed money to complete a transaction. For instance, if a trader wants to purchase $1,000 worth of Ethereum (ETH) at a leverage factor of 5x (or multiple of 5), they will only need to put down $200, with the remaining $800 coming from the exchange or trading platform. To put it another way, the trader took out a loan to multiply their position by 5. Equity is the worth of the account balance calculated using the current market price less the borrowed amount. Varying exchanges and trading systems have different maximum leverage limits.
Margin
The equity level fluctuates in real-time along with an asset’s market price. The trader will receive a margin call if the equity level falls below a certain level (also known as the margin requirement, which is set by the exchange or trading platform). In order to raise the equity value back up to the level where margin is required, they must then sell part or all of their position and/or add more of their own money to the account.
Collateral and Liquidation
When a trader applies for a loan, the assets in their account serve as collateral. The exchange or trading platform may sell the assets in the trader’s account (a process known as liquidation) and use the proceeds to settle the loan if the trader fails to meet a margin call.
Let’s look at an illustration of a margin call below:
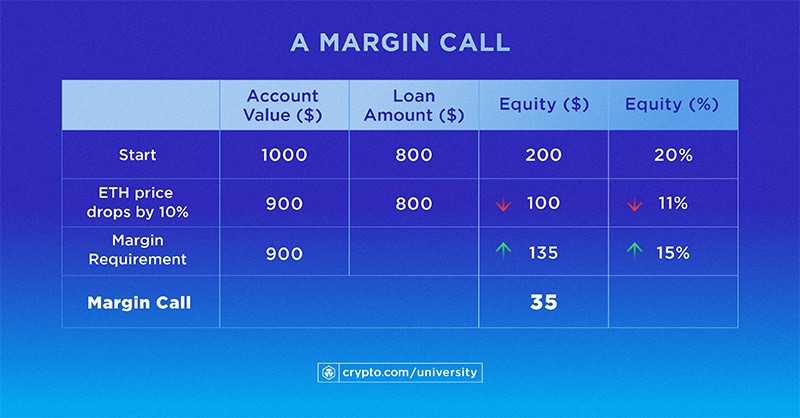
With a 5x leverage, the trader was able to purchase $1,000 worth of ETH by borrowing $800 and contributing $200 of their own money. The cost of ETH then decreases by 10%. If the exchange or trading platform requires 15% of the account value as margin, a margin call occurs because the equity level has fallen below that threshold.
To get the equity back up to the required margin, the trader will need to raise $35 by either selling some ETH or adding more of their own funds. The exchange or trading platform may be forced to sell the user’s ETH in the account to contribute to loan repayment if they are unable to fulfil the margin call.
Pros and Cons of Crypto Spot Trading
The key advantages of spot trading versus margin trading are that it is less complicated and does not have the potential to magnify losses. Because a trader doesn’t have to worry about things like margin calls and determining how much leverage to utilise, it is simpler. The trader does not run the risk of having to contribute more of their own money or of losing more money than they already have in their account because there are no margin calls.
The fundamental drawback of spot trading is that it is not able to take advantage of any potential return amplification that leverage might provide, which is covered in more detail below.
Crypto Margin Trading: Benefits and Drawbacks
The primary benefit of margin trading is the possibility of multiplying profitable returns when employing leverage. Let’s look at an example where a trader purchased one Ethereum (ETH) for $1,000 at a cost of $1,000, and then the price increased by 10% to $1,100.
The returns with no leverage and with leverage are shown below. Assume that in the leverage scenario, the trader employed a 5x leverage ratio (using $200 of their own money and borrowing the remaining $800). When employing leverage, the return is 50%, which is higher than when using no leverage, which is 10%.
| Scenario: ETH price up 10% | Return | Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| No leverage | +10% | (1100 – 1000) / 1000 |
| Leverage of 5x | +50% | (1100 – 800 – 200) / 200 |
Leverage, however, has a double-edged nature in that it can both enhance good and negative returns. Let’s suppose that the price of ETH decreased by 10% to $900 as opposed to increasing. In comparison to the return of -10% while employing no leverage, the return of -50% when utilizing leverage is much lower.
| Scenario: ETH price down 10% | Return | Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| No leverage | -10% | (900 – 1000) / 1000 |
| Leverage of 5x | -50% | (900 – 800 – 200) / 200 |
The potential for receiving margin calls is the other significant drawback of margin trading. This can require the trader to risk losing more than what they initially invested by adding more of their own money to the account, as previously mentioned.
Isolated margin and Cross Margin
Cross margin and isolated margin are two common applications of margin:
- Cross margin. This enables the trader to distribute margin balances among various positions, allowing for the use of excess margin (i.e., equity beyond the minimum margin need) from one position to make up for a margin shortfall in another. This might be utilised to help avoid forced liquidations of losing positions and/or margin calls.
- Smart cross margin. allows for offsets in the margin requirement for positions in opposing directions (such as long and short) and across various product classes (e.g., spot margin and futures).
- Isolated margin. This is the margin allotted to one slot, and it cannot be distributed among other positions. This is typically used by traders to prevent margin calls from one position from impacting other investments in their portfolio.
Spot vs. Margin: Which Should You Pick?
Two popular trading methods are spot trading and margin trading, which are used in markets besides cryptocurrency, such as equities, currencies, commodities, and bonds. The decision is greatly influenced by the risk tolerance and circumstances of the trader. The main distinction is that spot trading doesn’t involve leverage, but margin trading does.
Risk and reward frequently go hand in hand, thus margin trading may be a choice for people who are willing and able to accept more risk in exchange for the opportunity of potentially higher gains. Spot trading could be less hazardous and easier to execute for more traditional traders.
Exercise Due Diligence and Independent Research
This page solely includes samples for informational purposes. Any such information or other materials should not be interpreted as financial, investment, tax, or other advice. Nothing in this text should be interpreted as a solicitation, endorsement, or recommendation. Returns on the purchase and sale of cryptocurrencies may be subject to taxation in your jurisdiction, including capital gains tax.
Future performance cannot be predicted or guaranteed based on past performance. The value of cryptocurrency assets can rise or fall, and you run the risk of losing all or a sizable portion of your purchase price. You must conduct thorough study and due diligence before evaluating a crypto asset because any purchases you make are solely your responsibility.




