Nature isn’t classical, dammit, and if you want to make a simulation of nature, you’d better make it quantum mechanical, and by golly it’s a wonderful problem, because it doesn’t look so easy.
– Richard Feynman
Motivation and Introduction
Quantum Computing is a new paradigm of algorithmic study which extends quantum mechanical phenomena to the world of traditional computing. In 1982, Richard Feynman proposed an initial quantum computer, which would have the capacity to facilitate traditional algorithms with quantum circuits [1]. To understand systems of electrons and to navigate the multiple independent probabilities of electron location based on quantum phenomena, Feynman envisioned the concept of a quantum computer; he believed that quantum computers could ideally simulate quantum behavior as it would have occurred in nature. The quantum systems which Feynman wished to simulate could not be modeled by even a massively parallel classical computer. For example, let us consider the probability calculations of multiple particle systems. If we have two electrons constrained to being at two points (A and B), then there are 4 possible probabilities of their location (both at A, one A — one B, one B — one A, both at B, etc.). For 3 electrons, there are 8 probabilities, for 10 electrons, there are 1,024 probabilities, and at 20 electrons, there are 1,048,576 probabilities. Therefore, it is easy to see that measurements get out of hand for traditional physical systems with millions of electrons. Thus, research into quantum computers began and long-term goals for the field of quantum computing have arisen.
We will first discuss the mathematical background of quantum mechanics and notable quantum computers. We will then address the functioning of a quantum computer and its fundamental operators. We will finish the article by noting applications and the future directions of quantum computing.
Feynman explaining quantum mechanics at CERN [2]What does it mean for something to be “Quantum”?
“Quantum” is a term that comes from the study of Quantum Mechanics. Many a times, the term “quantum” is used as a buzzword in the field of particle physics. It is known that the modern relevance of something being quantum comes from the field of quantum mechanics. When one studies physics, they typically begin their journey in classical or Newtonian mechanics. They then progress to thermodynamics and statistical mechanics. Maybe later, they study topics in electromagnetism and photonics as well. After study of these subfields, we approach a new area of study colloquially known as modern physics. This includes topics in relativity and quantum mechanics. What is quantum mechanics? — it is the field of physics which tackles the physical properties of nature on an atomic scale. In our world as humans, we experience interaction and forces at a macro-scale. At the level of infinitesimally small particles (subatomic scale), the same principles of physics which govern our daily lives no longer apply. In other words, the rules are flipped and at a quantum scale, classical mechanics is insufficient. In a quantum system, all quantities are restricted to their discrete values (as part of quantization) and objects function as both particles and waves (wave-particle duality). It is critical to note that in a quantum environment, the value of a physical quantity can be predicted prior to its measurement if we are given the set of initial conditions (Heisenberg’s uncertainty Principle). Quantum mechanics was born when Max Planck proposed his situation to the black-body radiation problem and when Einstein presented his revolutionary theory on the connection between frequency and energy (later explains the photoelectric effect and general relativity).
Since this is not a physics-centered article, we will only discuss the fundamentals of quantum mechanics and the necessary mathematical notation. In summary, quantum mechanics provides four new phenomena: quantization, entanglement, principle of uncertainty, and wave-particle duality. Let’s begin by describing how objects function in a quantum system. Paul Dirac, David Hilbert, and John Von Neumann, and Hermann Weyl described the idea that the states in a quantum mechanical system are symbolized as “state-vectors.” Every quantum system has its own complex, separable Hilbert space. This acts as the state space of the system and is given to be a complex number of norm 1. Possible states are points in the projective space of a Hilbert space. Simply put, quantum particles can obtain the discrete eigenvalues of the Hilbert space since the eigenstate of the observable corresponds to the eigenvector of the operator.

Now that we know what a Hilbert Space is, let us discuss why quantum mechanics is known to be a probabilistic field. Quantum mechanics is all about the concept of measurement. The state of a system at a given time is described by a complex wave function due to wave-particle duality. In a quantum system, we can only measure probabilities of the results of experiments. For example, we could measure the probability of an electron being in region X of the electron cloud. Wave collapse is usually a issue when it comes to quantum measurement since the probability information of a system can collapse from the initial state to a particular eigenstate. Today, scientists bypass this issue through the use of quantum tomography, a technique used to reconstruct a certain quantum state via an ensemble of existing quantum states. Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle adds more to the sense of quantum particles existing as probabilistic functions since it references the idea that the operators which correspond to certain observables are not commutative and that there is a level of error associated with quantum particle movement.

While there is no one unifying theory which unifies all the fundamental forces of the universe as scientists continue to debate the validity and methodism of certain theories. General relativity, quantum electrodynamics, and supersymmetric string theory still come into competition with one another and it is an ongoing quest today to find the universal theory. Now that we have essentially designated the rigorous mathematical and physical background of quantum mechanical systems, we can move to draw insight on the world of quantum information and quantum computation. Without this background knowledge, it is difficult to proceed to discuss quantum computing in a technical light due to its dependence on the aforementioned physical phenomena. Simply put, quantum computing is a form of computation which extends the discussed properties to a linked software-hardware environment. Essentially, we live in a quantum world (nature is quantum by default), and quantum computers harness various properties to mimic such an environment.
What are Quantum Computers and how do they work?
Quantum Computing is the field that integrates quantum mechanical phenomena into a computing device. Quantum computers use properties like superposition and entanglement to perform computation. Different models of quantum computing exist — adiabatic quantum computers, Turing quantum computers, one-way quantum computers, etc. We will mainly discuss classical or digital quantum computing in this article rather than the aforementioned analog methods.
Qubits and Superposition
Let us start with the basics. Quantum information is data for quantum states which is utilized for the study of computational manipulation. This quantum information is processed in the form of “qubits”. Qubits can be thought of as the computational analog for bits and are the fundamental units of information for quantum computing. The qubit is described as a vector in the 2-dimensional Hilbert space. A traditional bit has 2 states (0 and 1). The state for a qubit also has 2 ground states – |0⟩ and |1⟩. This notation of using brackets comes from the earlier explained mathematical basis of quantum states. Remember that we earlier discussed that quantum states can be captured as probability functions and as state-vectors. The use of|0⟩ and |1⟩ reinforces this idea. The most basic states for a qubit are modeled below:

A qubit also has the ability to perform quantum superposition: it may hold multiple states at once. This is the first major quantum property which we can discuss. Superposition is instrumental to the operations of a quantum computer since it is what provides exponential speedups in both memory and processing speed for a quantum computer. The superposition of a qubit can be represented as a probability function dependent upon the amplitudes of the qubit in its Hilbert space (? and ?). A superposition of a qubit |?⟩ can be represented as the following:

Thus, we may represent each qubit as a linear combination of |0⟩ and |1⟩. ? and ? represent the amplitude probabilities and are typically complex numbers. When qubits are measured, they will follow the Born Rule:

To visually understand a qubit, we can understand it as a Bloch Sphere. This sphere shows the probabilities (? and ?) as being the determinate factors for the qubit and provides 3 degrees of freedom (originally 4 degrees of freedom but 1 is eliminated by the normalization constraint via the Born Rule). The two-dimensional Bloch Sphere visualization and feature map is shown below:

Quantum Registers
We may now discuss the importance of a quantum register. In a quantum computer, quantum registers are simply considered to be systems of multiple qubits. It is the quantum analog of a classical computing register. All quantum calculations are performed by manipulating qubits within the register. The quantum register has a size dependent on the number of qubits in its system. The Hilbert space of a quantum register expands with an increased number of qubits. We may mathematically represent a 2-qubit quantum register via the following:

The above mathematical description captures the concept of qubits via tensor products. The tensor product or Kronecker product combines the two quantum states of a qubit. The difference between a classical register and a quantum register is seen in the content of each respective environment. A classical register will store ? “flip-flops” while a quantum register will store ? qubits. Quantum registers also hold the ability to store data in a state of superposition. The states that a quantum register may access are known as Hilbert spaces with 2^n states. The Hilbert space is what gives a quantum computer the power to apply superposition on multiple qubits.
Quantum Gates
We know that classical computers manipulate bits through logic gates. Logic gates essentially transform the value that a bit holds. They are the building blocks of any digital system. Logic gates are used with truth tables to create transformations of state in classical circuits. A list of the most fundamental logic gates is given below:

In the world of quantum computing, the most basic quantum circuits are known as quantum gates. The same way that classical logic gates turn multiple binary inputs into a single outcome, quantum gates also manipulate binary inputs, except that now there are state-vectors involved. They deal with small pre-ordained amounts of qubits. These quantum gates are analogous to classical logical gates and follow similar patterns of logic. Complex quantum circuits are built through stacking and utilization of these quantum gates, similar to how classical logic gates are the building blocks for traditional computational circuits. However, unlike classic logic gates, quantum gates are reversible. Each quantum gate can operate on the collective Hilbert space of several bits. Thus, quantum gates possess the ability to change or modify the state of a certain system or quantum register. Quantum gates are mathematically represented by unitary matrices where the number of qubits in the input and output must be equal. A quantum gate (?) is mathematically defined below:

A quantum state which may be manipulated by a quantum gate are typically shown as “kets” or a bra-ket (|0⟩ and |1⟩.). We can model the transformation applied by a quantum gate (?) on a state (?) as the following:

This transformation multiplies the initial quantum state vector (?/) by the unitary quantum gate operator (?) to achieve a new quantum state (?0). Some common examples of gates are given below (Pauli-X, Pauli-Y, Pauli- Z, Hadamard, Phase, CNOT, CZ, SWAP, Toffoli):

These gates apply transformations on an initial system of qubits to map the basis state to a new value. For example, the Hadamard gate (?) maps the basis states of|0⟩ and|1⟩ to new values on the x and z axes. Similarly, other quantum gates like Pauli- X (?), Pauli-Y (?), Pauli-Z (?-?), and the Controlled Not (????) apply transformations that may be represented as unitary matrices. All of these transformations can also be visually recognized as shifts on the axis of a Bloch Sphere. For example, we can see the Pauli-X gate transformation mapped to the Bloch Sphere:

Entanglement
Another important quantum state which allows us to model quantum entanglement is the concept of the Bell States. The two Bell States (EPR pairs) represent two maximally entangled 2-qubits states:
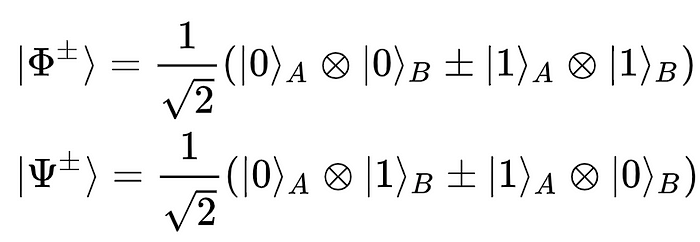
Together, these two Bell States form the Bell Basis or a maximally entangled basis of the 2nd dimensional Hilbert Space. This is the simplest example of quantum entanglement. Let’s talk more about what entanglement means. Quantum entanglement is when a pair (or group) of particles is generated in a way in that the state of one particle in the system cannot be described independently of the state of the others, including when the particles are separated by a large distance. Quantum entanglement is usually in reference to spatial proximity; it is also interesting to note that entanglement of two particles has been known to show that their spin, position, and polarization is correlated. Famously, Einstein referred to the phenomena of entanglement as “spooky action at a distance.” Entanglement is useful to quantum computing in that it can be used as part of quantum circuits to manipulate real-world data since correlations exists between real-world objects alongside those of a quantum system.
To summarize this section, we have broken down the fundamentals of quantum computing to its most basic operators. We have analyzed the two most essential aspects of quantum computing: superposition and entanglement. We have also covered qubits, quantum gates, registers, etc.
Modern Quantum Computing and its Applications
Inside a Quantum Computer
So far, we have only talked about the essential operators of quantum computing and its mathematical background and broad connection to physics. Let us now discuss the modern situation and the future directions of quantum computing. Let’s now take a peek inside a quantum computer. Here is a picture of a modern IBM quantum computer.

This obviously does not look like your everyday PC or desktop! There are millions of connections and over 2,000 components come together to allow researchers to work with qubits for a long period of time. The example above is specifically a superconducting quantum processor. In a quantum computer like this, any heat can introduce error into the system. Thus, it is regulated such that the machine always operates at subzero temperatures. Let’s review some of the specific components. The first component is the dilution refrigerator: this device exploits the mixing properties of two helium isotopes to facilitate a quantum environment. Why are the cold temperatures required? — they are needed in order to create a situation where qubits and their states will not experience quantum decoherence later. We will discuss what decoherence means later but for now, we can tie it back to the idea of quantum state collapse. Other components of the quantum computer include the qubit signal amplifier (cools stage to 4 Kelvin), input microwave lines (protect qubits from noise while extracting and sending input/output), superconducting coaxial lines (minimize energy loss when quantum states are transported), cryogenic isolators (allow progression of qubits without loss due to noise), quantum amplifiers (capture processor readout signals), and a mixing chamber (uses chemical components to cool apparatus) [11]. The main component of the machine — the superconducting processor — consists of a transmon qubit (uses supercharge and maintains qubit control without noise) and Josephon junctions (allows supercharge to flow through the machine). This information is a lot to digest but just understand that quantum computers are intensive machines which require low temperatures and a superconducting processor to function.
Applications
Well, we know that quantum computers are great because of their properties like superposition and entanglement. However, it is important to realize that we live in a quantum world and that quantum computers will allow us to better simulate the behavior of nature, down to a molecular level. For example, we can now make breakthroughs in drug development and medicine. For instance, look at the Caffeine molecule. For scientists, it currently requires too much processing power to appropriately simulate this molecule and to analyze its structure. With quantum computing, scientists may be able to better simulate the caffeine molecule and its true behavior at the molecular scale in the presence of quantum factors. Beyond medicine and chemical analysis, quantum computing is also useful for applications in several other fields. It can be used to accelerate AI and machine learning to better understand patterns in data. It can be used in finance to build more ideal portfolios and assess the market. It can be used in robotics and precision control theory to navigate complex spaces. Overall, quantum computing is great for optimization and modeling in general. Thus, even though we are not at fault tolerance yet (discussed later), as the numbers of qubits increase, quantum computers can have their applications extended to numerous industries.
Quantum Computing in the News Today
Many of us have heard about quantum computing in both a positive and negative light. We have shown that properties like superposition and entanglement allow quantum computers to have exponential speedups in terms of both execution time and memory. Let’s first discuss the positives of quantum computing. There are several storylines about how quantum computing is the future of computational power and abilities. Recently, google announced that they had achieved “quantum supremacy” with a quantum processor known as Sycamore (referenced below).

According to Google, quantum supremacy means that their quantum processor was able to perform a certain task rapidly (within seconds) when a it would take a classical computer tens of thousands of years (making it an unreasonable problem). While the validity of this supposed milestone is debated, there has been a general consensus that the field of quantum computing is rapidly expanding. If quantum computing becomes advanced enough soon, it can revolutionize all areas of technology and any field where computational modeling or data processing is required due to the efficiency standard that it brings to the table. Maybe one day, decades from now, air traffic requests and control is managed by an intelligent, low maintenance quantum system. However, breakthroughs like these are decades away due to the current lack of fault tolerance. We discuss this more in the next subsection.
It is also well known that quantum computing poses an immediate cybersecurity threat due to this dramatic increase in processing power. Most of modern encryption is RSA or public key encryption. For classical computers, cracking these encryptions schemes is an unreasonable problem that will take thousands of years. As quantum computers grow to handle more qubits and gain access to greater amounts of exponential speedup, it will eventually be possible for quantum computers to crack these encryption methods and the private data of millions if not billions of users will be leaked. This would be detrimental to society and thus quantum computation will require some amount of regulation to proceed safely. Check out this guide for more on how quantum computing can change cybersecurity forever.
Quest for Fault Tolerance
Until fault tolerance is achieved, quantum computers will essentially be bottlenecked due to performance constraints and constant decoherence. Remember that decoherence is the idea that there is a partial collapse of quantum information. In these situations, any further measurements give the same result (state is unable to change) and we are unable to measure a particle’s position or velocity in respect to the outside world. Fault tolerance is the idea that a quantum computer will be manage to operate at essentially negligible noise. A fault tolerant quantum computer will be successful at avoiding the “uncontrollable cascade of errors caused by the interaction of quantum-bits, as these concepts can be directly mapped to quantum information.” [12] The idea that fault tolerance is necessary is reinforced in the quantum threshold theorem. This theorem states that if a quantum computer has a massive number of qubits (> 10,000) and if it is able to apply a “depolarizing quantum error correction scheme” to limit noise to under 1%, it has achieved a degree of fault tolerance. In simple terms, to approach a fault tolerant quantum computer, we essentially need to correct errors at a rate faster than they occur. This is incredibly difficult (exponential in fact) and can only be done with thousands of qubits at minimum. At the time of the writing of this article, quantum computers like Google’s Sycamore can only process between 50 and 60 qubits at maximum capacity. Moreover, until we achieve fault tolerance, quantum computers and their results will be severely limited as a result of the noise and perturbations which they experience. This is one of the biggest obstacles in the quantum computing field and it will most likely take a few decades until major progress is made towards a fault tolerant quantum computer. However, we can still make strides in terms of the efficiency of quantum algorithms and in terms of the quantum error correction schemes which are employed.
How you can get involved
While it may seem like quantum computing is the last field where students and researchers may be able to get started relatively easily, this is not the case. You can pick up quantum computing basics and get hands-on experience with these machines. The IBM Quantum Experience is a great place to get started since it allows users of all backgrounds and expertise to tinker with quantum computing through the design of quantum circuits. It is simple to use and feels almost like a drag-and-drop interface where users can use different amounts of qubits in the initial register and apply various gates to see how they affect the state-vectors of the qubits. Another way to get started with quantum computing is to use Qiskit. Qiskit is a python library that allows users to play with popular quantum algorithms and design their own. It can be used in a jupyter notebook inside IBM Q and can be used to implement algorithms like Shor’s algorithm, Grover’s algorithm, etc. I have linked the Qiskit starter guide and textbook here, so that you can get started!
Kudos to you for working through this article. You already have grasped a solid amount of quantum mechanics, mathematics, and quantum computing, and I recommend that you try to learn even more about quantum computing! Note that this only an introductory guide and by no means comprehensive, so feel free to explore more as there are so many cool opportunities and interesting applications to consider in this field!
Thanks for your time and here is a great final quote to end on …
Quantum computation is a distinctively new way of harnessing nature. It will be the first technology that allows useful tasks to be performed in collaboration between parallel universes.
— David Deutsch
References
Some of the content for this article is borrowed from a short research paper that I wrote.
Medium Articles which I cite:
Jason Roell: https://towardsdatascience.com/the-need-promise-and-reality-of-quantum-computing-4264ce15c6c0
Arun C: https://towardsdatascience.com/quantum-computing-explained-a114999299ca
Jason Roell: https://towardsdatascience.com/quantum-computing-and-ai-tie-the-knot-d4440267451b
Egor Dezhic: https://towardsdatascience.com/the-present-and-future-of-quantum-computing-for-ai-fb600546bbb7
Rishabh Anand: https://towardsdatascience.com/quantum-computing-with-colorful-diagrams-8f7861cfb6da
[1] Feynman, R.P.: Simulating physics with computers. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 21(6), 467–488 (1982)
[2] Image — Feyman at CERN: https://www.sciencephoto.com/media/898764/view/richard-feynman-s-post-nobel-lecture-at-cern-1965
[3] Image — Hilbert Space: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/312590429_A_simple_proof_of_Born%27s_rule_for_statistical_interpretation_of_quantum_mechanics/figures?lo=1&utm_source=google&utm_medium=organic
[4] Image — Particle-Wave Duality and Heisenberg’s Uncertainity Principle: https://science.howstuffworks.com/innovation/scientific-experiments/10-scientific-laws-theories10.htm
[5] Havlicek et al. -> Image — Bloch Sphere: https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.11326
[6] Image — Logic Gates: http://www.justscience.in/articles/how-are-logic-gates-related-to-circuits/2017/06/01
[7] Image — Quantum Logic Gates: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quantum_logic_gate#/media/File:Quantum_Logic_Gates.png
[8] Image — Pauli Gate:
[9] Image — MIT Technology Review: https://www.technologyreview.com/2020/02/26/916744/quantum-computer-race-ibm-google/, https://www.technologyreview.com/2019/01/29/66141/what-is-quantum-computing/
[10] Image — Google Blog: https://ai.googleblog.com/2019/10/quantum-supremacy-using-programmable.html
[11] IBM Quantum Computer Components: https://www.ibm.com/quantum-computing/learn/what-is-quantum-computing/
[12] Fault Tolerant quantum computation with few qubits: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41534-018-0085-z
This article has been published from the source link without modifications to the text. Only the headline has been changed.




